Digital Radiography: 3 Notable Advancements
Modern diagnostic radiography and imaging’s foundation was created over a hundred years ago after Wilhelm Röntgen, a German scientist, initially observed X-rays back in the late 1800s and was awarded a Nobel Prize for the discovery. But these days, the radiography field is being transformed by digitization.
In the last few years, there have been many advancements in digital radiography, including but not necessarily limited to AI-aided interpretation for X-ray, tomosynthesis, dual-energy imaging, and more. They improve the quality of the images, enhance the care for patients, and support better outcomes. Moreover, digital radiography can minimize, if not diminish, retakes lowering radiation exposure.
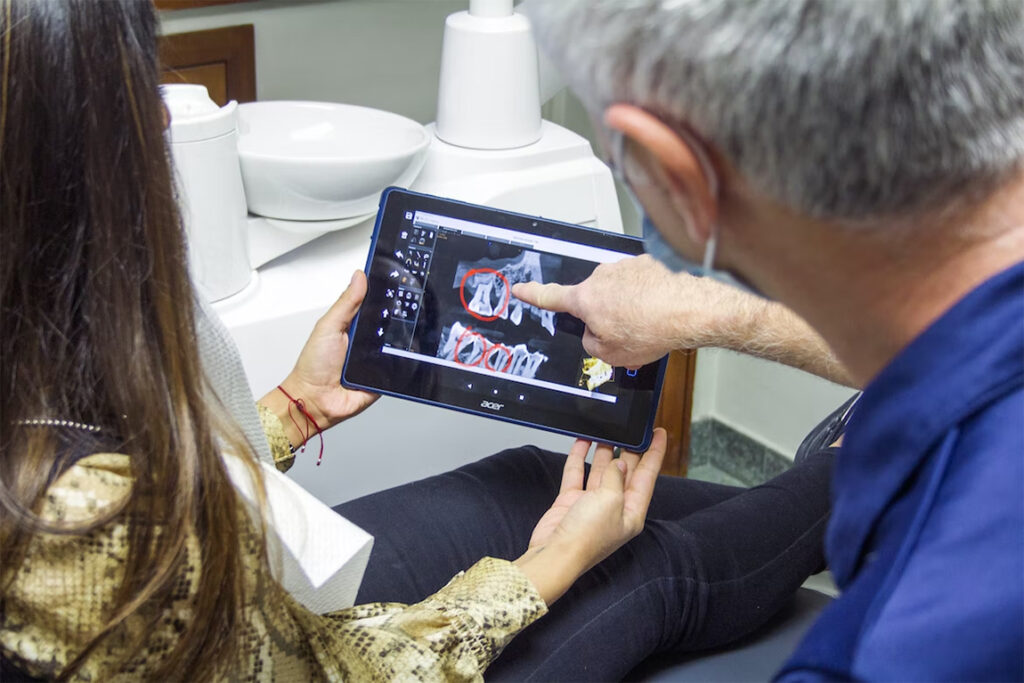
1. AI-driven X-ray interpretation
X-ray interpretation driven by artificial intelligence has evolved over the last decade, especially when it comes to chest radiography. And one of the most common imaging examinations, specifically in most emergency departments. And it continues advancing in various areas.
- AI-driven X-ray interpretations have been used for diagnosing the COVID-19 virus. According to some studies, artificial intelligence-assisted assessments of chest x-rays can aid radiologists in differentiating negative and positive patients and improve diagnosis precision significantly.
- Other studies published also found AI algorithms to perform well when it comes to chest radiographs’ preliminary interpretations. The findings determine that AI can improve workflows in radiology, strengthen accuracy for precise diagnoses, address concerns regarding resource scarcity, and drive down healthcare costs.
2. Dual-energy imaging
Dual-energy imaging, or spectral CT as it’s commonly known, is a kind of computed tomography practice that makes use of two distinct photon energy X-ray spectra, enabling the interrogation of various materials that may have attenuation properties that differ from each other at an energy level. While traditional single-energy CT generates single image sets, dual-energy can be utilized to construct numerous types of images, including:
- Average weighted imaging
- Virtual monoenergetic imaging
- Material decomposition imaging
- Effective atomic numbers
- Electron density mapping
Thanks to current-generation technology with quicker processors, the rapid analysis and acquisition of data have become possible, increasing dual-energy imaging’s adoption in the healthcare community. Some of the cases in which it may be used are the generation of quality images for blood vessels, reducing examination numbers that patients need to undergo, improving the image’s quality, detecting abnormalities, and so forth.
3. Computer-aided diagnosis
Computer-aided diagnosis, or CAD, is at computer science and medicine’s intersection. It’s a digital radiography form designed primarily to facilitate medical experts’ diagnostic decisions. Imaging techniques like CT, ultrasound diagnostics, MRI, and X-rays provide valuable data that radiologists can use to evaluate and analyze cases. In many situations, the urgency to get results, radiologists need to understand the images quickly, and the advancements in CADs have made it possible for them to interpret images much faster than they otherwise would have.
Conclusion
Advancements in digital radiography’s field have made it possible for medical practitioners to deliver a higher level of healthcare service and produce better results for their patients, as it enables them to make accurate diagnoses in a shorter time frame. As these technologies continue to evolve, not only are we more likely to see more positive patient outcomes, but also much easier work for healthcare providers..