New Wearable Will Turn Your Body Into a Battery

Almost everyone is complaining about the life of a battery, which powers most mobile electronic devices and medical devices. This is understandable considering that some batteries only last less than 24 hours while others have power for at least three days.
But what will you say when you can use your own body to generate power and become your personal battery?
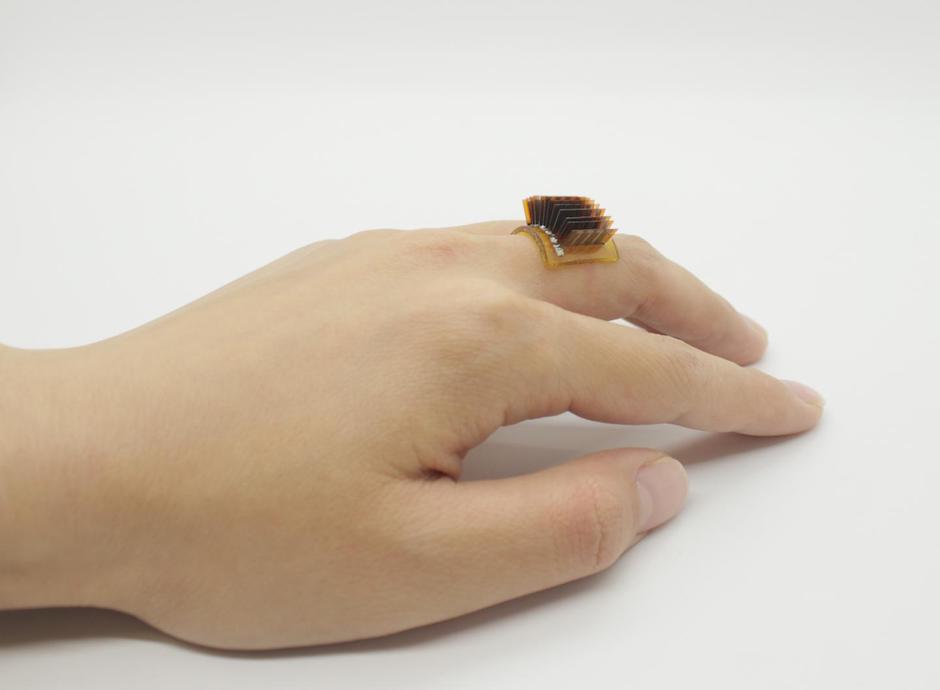
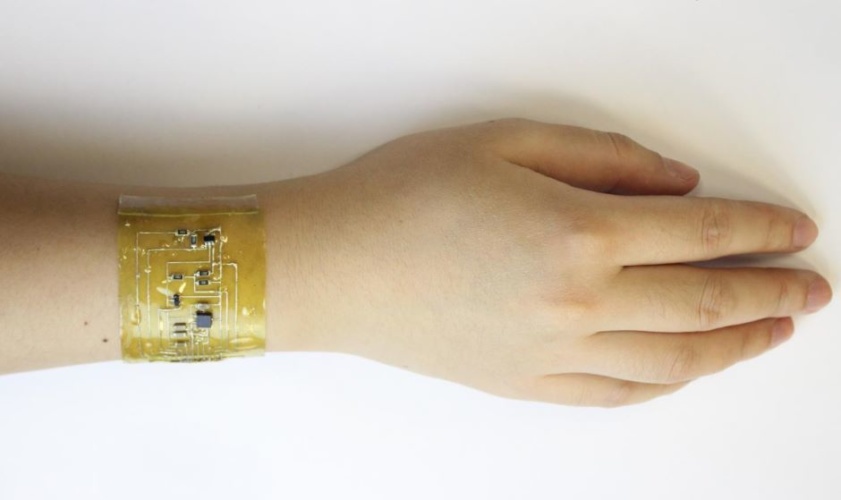
This is not fiction. A team of engineers from the University of Colorado Boulder published their research paper in the journal Science Daily in February 2021 about their creation of a wearable device, either as a ring or bracelet or something else that will touch the skin. The device will harvest the natural heat from the wearer’s body and turn it into electricity using thermoelectric generators.
Innovation
There were similar experiments before about thermoelectric wearable devices, but the material the scientists used was rigid.
In the latest experiment, the scientists of the University of Colorado Boulder, used another base material. Senior author of the research paper and associate professor at the mechanical engineering department, Jianliang Xiao, said that they used polyimine, an organic compound that is stretchy, self-healing, and recyclable. The professor further explained that the thermoelectric device they developed can be worn next to the skin.
Currently, the device can generate about one volt of energy per square centimeter of skin. It is enough to provide power to fitness trackers and watches.
Creating the wearable biological battery
In creating the device, the scientists attached a series of thin thermoelectric chips into the polyimine and connected them with liquid metal wires, creating a stretchable device that does not strain the thermoelectric material. Attached to the body, the device uses the heat that the body usually dispels.
According to Professor Xiao, they can increase the power of the wearable battery by adding more blocks of generators. According to their calculation, a person doing some brisk walking could produce around five volts of electricity by wearing a device the size of a sports wristband.
The research team is looking at their device’s application
for many medical devices, such as drug delivery pumps and pacemakers that rely
on batteries
to keep working.
For items that require more power, the professor said that the device can be
made to cover more areas, as long as it can have close contact with human skin.
Electronic skin
Creating something innovative and useful is something Professor Jianliang Xiao has done in the past. His team also created the electronic skin that is as elastic as biological tissue, which can likewise heal itself. Their research on electronic skin was published in the Science Daily Journal in November 2020.
Professor Xiao and his team have announced their work on creating an electronic skin in 2018. They have made a lot of improvements to their concept within two years, one of which is making the artificial skin more elastic and functional.
What they did was to print a network of liquid wires and sandwiched the wires between two thin films of polyimine. The skin they created was a little thicker than a commercial adhesive tape used to cover small cuts and wounds.
The device can be applied to the skin using heat. Another significant thing about the device is that it can be stretched by about 60% of its size in any direction without disturbing the wire network.
They used the same material they used for the electronic skin to create the battery. Thus, the device also exhibits the same properties – stretchy, flexible, and self-healing. If a tear develops, the wearer only has to pinch the broken parts together. The professor said that the tear will be fully repaired within 13 minutes. The research team said that they still have many things to work on to improve the device, but they are looking at the number of applications that can use the biological battery. They are very optimistic that devices using their technology will appear in the market within five to ten years.