Magnetic Prosthetic Hands: A Breakthrough in Natural Movement for Amputees
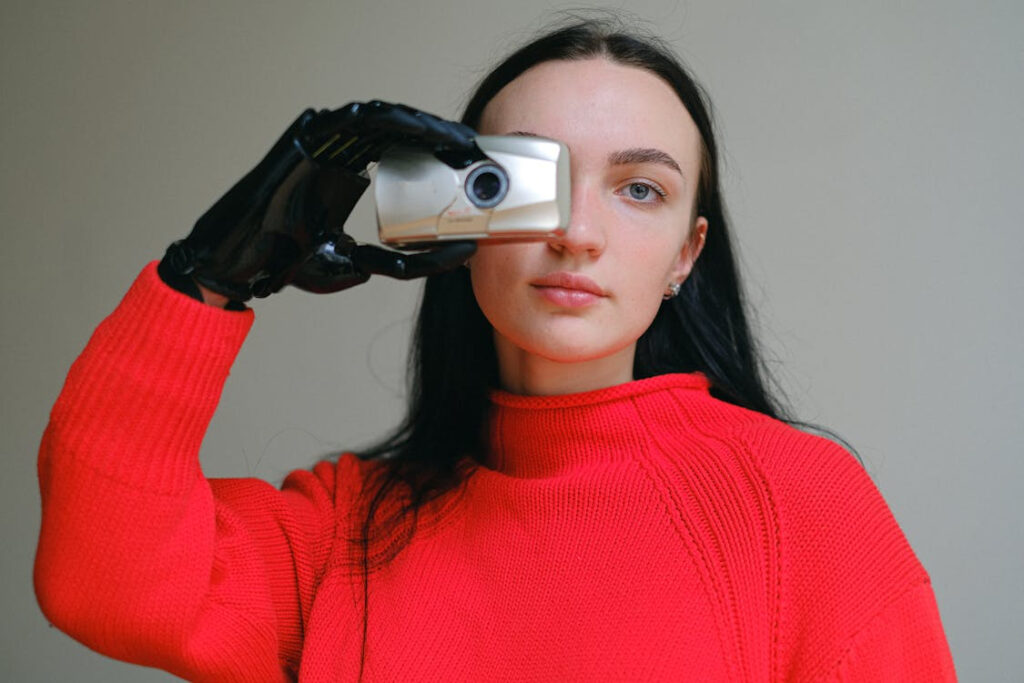

With the creation of magnetic prosthetic hands allowing amputees to perform natural hand motions by just thinking, prosthetic technology has advanced remarkably. Based just on tiny implanted magnets and muscles, researchers at the BioRobotics Institute of the Scuola Superiore Sant’ Anna in Pisa have developed a device that replaces the need for cables or electrical contacts. By restoring not only capability but also the sensation of control over their prosthetic hands, this development could change the life of amputees.
The Power of Myokinetic Control
At the core of this revolutionary prosthetic technology is myokinetic control, a system that decodes motor intentions through implantable magnets placed in the residual muscles of an amputated arm. These magnets respond to muscle contractions, allowing patients to control their robotic fingers with precision. The system was successfully tested on a patient named Daniel, who had lost his left hand. By using magnets to detect muscle movements, the prosthesis translates these signals into commands for everyday tasks like gripping a glass or opening a jar, demonstrating unprecedented natural control.
From Concept to Patient Trial
The journey from concept to real-world application involved extensive research and meticulous testing. Daniel, the first patient to undergo this trial, had magnets implanted in his arm in April 2023. During the surgery, the medical team carefully identified the residual muscles, isolating them for magnet placement. The surgical process required adaptation due to scarring and fibrosis, but the team successfully completed the implant. Following the procedure, Daniel was able to operate the prosthetic hand smoothly, performing tasks that require both strength and delicate handling, such as cutting with a knife or zipping a jacket.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Apart from the physical rehabilitation of hand motions, the magnetic prosthesis provides amputees such as Daniel with an emotional support system. Patients who can precisely manipulate a prosthetic limb might restore sensations they lost, therefore forging a close psychological link with the tool. Emphasizing the great influence this invention can have on mental health and emotional well-being, Daniel said using the prosthetic hand felt like moving his own hand again. The outcome of this trial gives many more amputees striving to restore confidence and mobility hope.
Later on Evolution of the Technology
Beyond specific situations like Daniel’s, magnetic prosthesis has transforming power. Determined to use this technology to help a greater spectrum of amputees, Professor Christian Cipriani and his colleagues European and national grants support continuous research meant to improve the system for different kinds of amputations. This development could quickly transform prosthetic medicine by allowing more patients to gain from the smooth integration of magnetically controlled devices, therefore enhancing the quality of life for many people worldwide.
Offering amputees natural, intuitive control over their robotic limbs, the creation of magnetic prosthetic hands represents a major breakthrough in prosthetic medicine. Following a successful experiment of myokinetic control, scientists have shown that implanted magnets are feasible in restoring hand motions. As the technology develops and more people in need are reached, this innovation could help many people to live better.