Going Big: The Applications of Nanotechnology Extensively Benefit Mankind
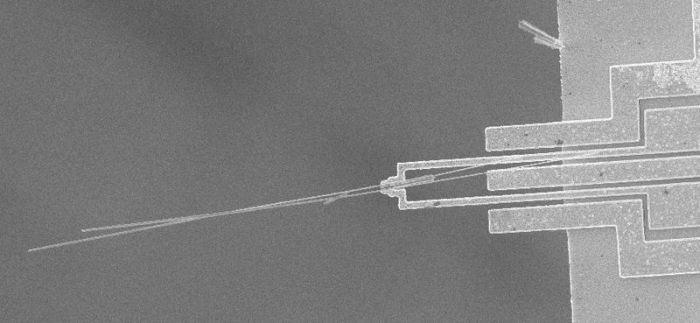
Nanowire sample by Erik Bakkers; SEM image by Kristian Mølhave; Microgripper på MIC (Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic)
Various nanotechnology-related articles have been written on this blog before, each presenting the recently developed ways of applying nanotechnology for the benefit of mankind. However, there hasn’t been a post that comprehensively discusses the useful applications of nanotechnology. It should be worth the space on this blog to present viable nanotechnology uses not only based on recent R&D outputs but including those that have been developed in the past years that may have already found their way in actual products available to consumers.
Nanotechnology in Medicine and Biotechnological Applications
Nanotechnology’s applications in medicine and biotechnology appears in a variety of forms, broadly referred to as nanomedicine. This aspect of nanotechnology application can be divided into a number of categories, briefly described below:
Nanotoxicology – As the term implies, this is about using the principles of nanotechnology to understand and find the applications of nanomaterials’ different toxicity levels. Nanotoxicology is centered on ensuring that nanomaterials are used at levels or ways that don’t affect human life and the environment. An example of this is the study entitled “Assessing the In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles” published in the journal Chemical Reviews.
Nanosensors – Through nanotechnology, very tiny sensors are produced and used in biological, surgical, and chemical applications. At present, there aren’t that many biosensors used in the field of medicine although the predicted applications of this technology are quite a multitude. Nanosensors are currently being used to measure the mass of an attached particle and chemical sensing.
Nanoshell – Nanoshells are spherical nanoparticles made of a dielectric core and a metallic shell. They involve a quasiparticle similar to the quantum droplet we wrote about before. One of the most significant applications of nanoshells is cancer treatment. They can be used to attach to cancerous cells and improve bio-imaging and induce photothermal ablation to kill cancer cells.
Nanorobotics – In broad terms, nanorobotics refers to the creation of robots that are so small they are measured by nanometer. At present, the most viable use of nanorobotics is the diagnosis cancer and the targeted drug delivery for the treatment of the disease. In the future, it may also become possible for nanorobots to undertake surgeries or other forms of treatments at the cellular level.
Nanobiotechnology – Also known as bionanotechnology and nanobiology, nanobiotechnology refers to the study and development of nanodevices, nanoparticles, and phenomena on the nanoscale to address questions or problems encountered in the field of biotechnology. Essentially, the term means a highly miniaturized concept of biotechnology.
Nanotechnology in Sustainable Technology
Nanotechnology can also be employed to enable sustainable processes or technologies. One example of this is the use of nanotechnology to improve the efficiency of solar panels. Nanotechnology has led to the development of hydrophobic and self-cleaning coatings for photovoltaic and solar thermal panels. Likewise, nanotechnology can be used for water treatment, to sift out contaminations of toxic metal ions, microorganisms, and organic and inorganic particulate matter found in wastewater and groundwater intended for human consumption. Moreover, nanotechnology can help address the problem of pollution. Researchers are exploring the possibility of using buckminsterfullerene in controlling pollution with its ability to control certain chemical reactions.
Nanotechnology in Energy Tech
Even the energy sector benefits from nanotechnology. Aside from the efficiency enhancement in photovoltaic cells mentioned earlier, nanotechnology also brings forth enhancements to energy production and consumption in various forms, as summarized below:
- Faster charging and higher capacity batteries
- Reduced energy consumption through improved efficiency by using lighter materials and innovative systems like quantum caged atoms
- Increased energy production efficiency especially in internal combustion engines
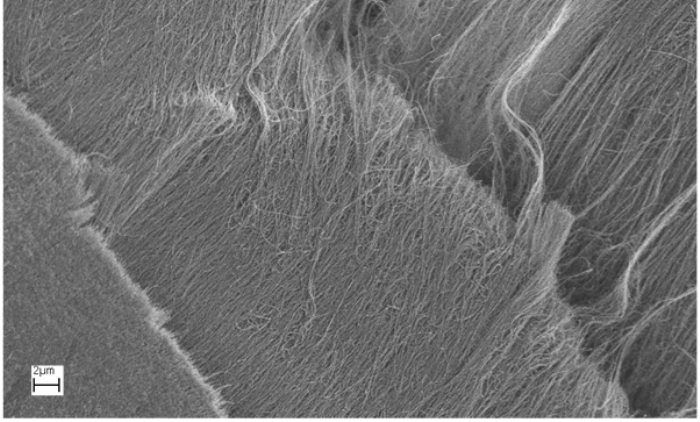
Illustration by Kristian Molhave made for the Opensource Handbook of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic)
Industrial Applications
Of course, nanotechnology also offers a host of industrial applications. These include the fields of food production, consumer goods production, aerospace and vehicle manufacture, military applications, and various types of construction projects. In food production, nanotechnology-based biosensors and packaging systems ensure that food is produced in safe and efficient ways. In the area of consumer goods, there are various nanotech-based surfaces and coatings used in producing a wide range of products, from household cleaning supplies to appliances, toys, and optics. Needless emphasizing, vehicle and aerospace related manufacturing also benefit from nanotechnology with its ability to come up with lighter and high efficiency components. The same goes in the field of military applications. Nanotechnology has paved the way for more advanced biological sensors, stronger equipment and combat gear material, improved medical care devices, and more sophisticated weaponry. For the construction industry, nanotechnology also offers advantages similar to the benefits enjoyed in the fields of vehicle manufacture and the military use of nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology is becoming a very useful technology that provides benefits through an extensive array of applications. Right now, scientists are only uncovering a fraction of nanotechnology’s full potentials. It’s exciting to anticipate what more can biotechnology bring for the benefit of everyone.
![By NASA (Great Images in NASA Description) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://techtheday.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/nanogears.jpg)